| Contents |
|
| General | Back to top |
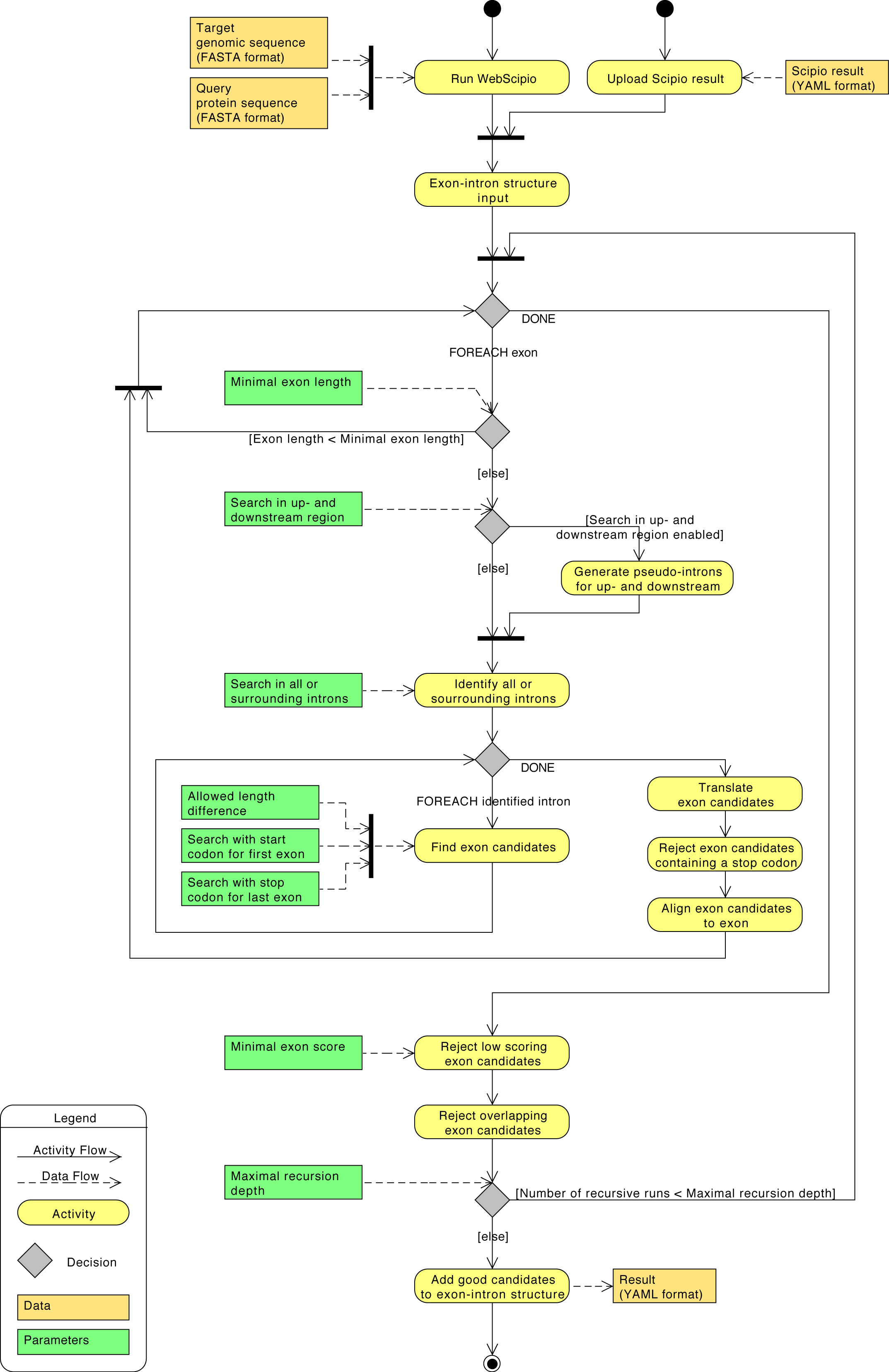
WebScipio offers an advanced option to search for mutually exclusive spliced exons. It is based on the exon-intron structure determined by Scipio. The algorithm of the search divides into several steps, which are conducted for each known exon. It takes three assumptions into account: Firstly, mutually exclusive spliced exons have a similar length; secondly, their splice sites and reading frames are conserved; thirdly, they are homologues. Several parameters of the search are adjustable.
| Options | Back to top |
Allowed length difference for exons
Determines the maximal difference between the length of an exon and the length of the corresponding alternative exon. The length is defined by the number of amino acids per exon.
Minimal score
The score is defined by the global alignment of the translated exon sequence to the corresponding alternative exon translation divided by the global alignment of the exon translation to itself. The minimal score is a threshold above which the alternative exon is taken into account.
Minimal exon length
Just exons, which are longer than the minimal exon length, are taken into account for the mutually exclusive spliced exons search. The length is defined by the number of amino acids of the exon.
Search in up-/downstream region
This option defines whether the algorithm should search for alternative exons in the up- and downstream region of the gene. The length of the up- and downstream region must be included in the Scipio result and is determined by the Scipio option "Region Size".
Search with start codon for first exon
The first exon does not have a splice site at the 5' end but its beginning is determined by the start codon (ATG) coding for a Methionin. So the algorithm tries to find alternative exons beginning with ATG (and not with a splice site at the 5' end of the exon).
- Auto (Search with start codon if first exon begins with start codon and is start of protein sequence): This option makes it possible to autodetect, whether the first exon in the Scipio result is the beginning of the protein. It searches for alternative exons with ATG start codon (instead of splice site) if the first exon begins at the start of the protein sequence and starts with ATG.
- Search with start codon (ATG) for first exon: This option forces the algorithm to look for alternative exons with ATG as start codon for the first exon (and does not use the splice site).
- Search with splice-site pattern for first exon (recommended for partial genes): This option forces the algorithm to use splice sites of the first exon to look for alternative exons as if it is a normal exon in the middle.
- Disable (don't search for alternatives of first exon): This options diables the search for alternatives of the first exon.
Search with stop codons for last exon
The last exon does not have a splice site at the 3' end but its end is determined by a stop codon (TAG, TAA, TGA). So the algorithm tries to find alternative exons followed by a stop codon (and not with a splice site at the 3' end of the exon).
- Auto (Search with stop codons if last exon is followed by a stop codon and is end of protein sequence): This option makes it possible to autodetect, whether the last exon in the Scipio result is the end of the protein. It searches for alternative exons with stop codons (instead of splice site) if the last exon ends at the end of the protein sequence and is followed by TAG, TAA or TGA.
- Search with stop codons (TAG, TAA, TGA) for last exon: This option forces the algorithm to look for alternative exons followed by stop codons for the last exon (and does not use the splice site).
- Search with splice-site pattern for last exon (recommended for partial genes): This option forces the algorithm to use splice sites of the last exon to look for alternative exons as if it is a normal exon in the middle.
- Disable (don't search for alternatives of last exon): This options diables the search for alternatives of the last exon.
Maximal recursion depth
The maximal recursion depth determines the number of recursive runs. In a recursive run the search is started again with the found alternative exon candidates as start points. Then the parameters are applied to the new exon candidate in contrast to found candidates of this new one. to
| Examples | Back to top |
Daphnia pulex Mysion Heavy Chain (Mhc) gene with 9 clusters of mutually exclusive spliced exons
| Organism | Daphnia pulex |
| Genome file | |
| Query sequence | MPPKKDMGPDPDPAQYLFVSLEMKRADQTKPYDGKKATWVPCEKDSYQLGEITGTKGDLV VVKVADGNEKMVKKDQCFPVNPPKFEKVEDMADLTYLNDAAVLHNLRQRYYHKLIYTYSG LFCVAINPYKRFPIYTQRVIKMYIGKRRNEVPPHIFCISDGAYMDMLTNHENQSMLITGE SGAGKTENTKKVIQYFAQIAKDTKGSKHTFSSGGNLEDQIVQTNPVLEAFGNAKTTRNDN SSRFGKFIRIHFGNSGKLAGADIETYLLEKARVISQQALERSYHIFYQIMSGKLPTLKAD CCLVDDIYQYNFVSQGKITIPSMDDSEEMALTDEAFEILGMGEQRPEIWKITAAVMHFGT MKFKQRGREEQADPDGTQEGENVAKMMGVDGPQLYMNFLKPRIKVGNEFVTQGRNVNQVV YSIGAMAKAIFDRLFKWLVKRVNETLETGQKRVTFIGVLDIAGFEIFDYNGFEQLCINFT NEKLQQFFNHHMFVLEQEEYKKEGIDWVFMDFGMDLQACIELMEKPMGVLSILEEESMFP KATDQTFAEKLNNNHLGKSASFVKPKPAKAGCKEAHFAIAHYAGTVPYNITGWLEKNKDP LNDTVVDQFKKGSSKLVQEIFADHPGQSGGKEEAKGGKRTKGSGFQTVSALYREQLNGLM KTLNATSPHFIRCIIPNETKSPGVIDSHLVMHQLTCNGVLEGIRICRKGFPNRMVYPDFK HRYMILAPNEMKAEPDERKAAKICLEKIALDPEWYRIGHTKVFFKAGVLGQLEEMRDDKL AKIITWMQSFIRGYHTRKQYKQLQDQRVALCVVQRNLRSYLQMRTWAWYRLWQKVKPLLN VTRVEDEIKALEDKAAAAQANFEKEEKLRKELETNLAKLTKEKEDLLNRLQAESGTVADF HDKQNKLMSQKADLESQLSDTQERLQQEEDARNQLFQNKKKLEQEASGLKKDIEDLELAL QKTETDKATKDHQIRNLNDEIAHQDELINKLNKEKKHMQEVNQKTAEDLQASEDKVNHLN KVKAKLEQTLDELEDSLEREKKLRADIEKNKRKTEGDLKLTQEAVADLERNKKELEQTIQ RKDKEIASLNAKLEDEQSLVGKLQKQIKELQSRIEELEEEVEAERQARAKAEKQRADLAR ELEELGERLEEAGGATAAQIELNKKREAELSKLRRDLEESNIQHESVLSNLRKKHNDAVS EMSEQIDQLNKMKAKAEKDRSQFAGENNDLRAAMDHVSSDKAAAEKMTKMLQQQLNEIQS KLDEANRSLNDFDVQKKKLTIENSDYLRQLEDAESQVSQLQKLKISLTTQLEDSKRMADE EGRERATLLGKFRNLEHDIDNIREQLDEESEAKADLQRQLSKSNADCQMWRHKYESEGVA KAEELEDAKRKLQARLGEAEEAIESLNQKNVALEKIKMRLSGELDDMHVEVERATVLANQ MEKRGKNFDKVVSEWKAKVDDLAAELDASQKECRNYSTELFRLKAGYDESQEHLEAVRRE NKNLADEIKDLMDQIGEGGRNVHEIDKQRKRLEVEKEELQAALEEAESALEQEENKVLRA QLELSQVRQEIDRRIQEKEEEFENTRKNHQRAIDSMQASLEAEAKGKAEALRMKKKLESD INELEIALDHANKANAEAQKSIKRYQQSIKETQSALEEEQRNRDDLREQYGIAERRANAL QGELEESRTLLEQADRARRQAETELADAHEQLHDLTAQAASSSAAKRKMESELQTLHADL DDMINETKNSEEKAKKAMVDAARLADELRAEQEHAQAQEKQRKALELQVKELQVRLDESE NNALKGGKKAIQKLEERVRGLETELDGEQRRHADAQKNLRKSERRIKELTFQSDEDRKNH ERMQDLVDKLQQKIKTYKRQIEEAEEIAALNLAKFRKAQQELEEADERAELADQAVSKLR AKGRGGSASRLSPPPQMKPRSKRDFE |
| YAML-file for upload | |
| Expert options | defaults, except "BLAT Tilesize = 6" |
| Search for mutually exclusive exons | defaults Enable search! |
| Result |

|
Drosophila melanogaster DSCAM gene with 4 clusters (12, 47, 32, 2) of mutually exclusive spliced exons
| Organism | Drosophila melanogaster |
| Genome file | |
| YAML-file for upload | |
| Query sequence | MNMPNERLKWLMLFAAVALIACGSQTLAANPPDADQKGPVFLKEPTNRIDFSNSTGAEIE CKASGNPMPEIIWIRSDGTAVGDVPGLRQISSDGKLVFPPFRAEDYRQEVHAQVYACLAR NQFGSIISRDVHVRAVVAQYYEADVNKEHVIRGNSAVIKCLIPSFVADFVEVVSWHTDEE ENYFPGAEYDGKYLVLPSGELHIREVGPEDGYKSYQCRTKHRLTGETRLSATKGRLVITE PVGRVSPKFPNTLTSSSFTGDEGSSQTLLCPAQAYPAPLFRWYKFIEGTTRKQAVVLNDR VKQVSGTLIIKDAVVEDSGKYLCVVNNSVGGESVETVLTVTAPLSAKIDPPTQTVDFGRP AVFTCQYTGNPIKTVSWMKDGKAIGHSEPVLRIESVKKEDKGMYQCFVRNDQESAEASAE LKLGGRFDPPVIRQAFQEETMEPGPSVFLKCVAGGNPTPEISWELDGKKIANNDRYQVGQ YVTVNGDVVSYLNITSVHANDGGLYKCIAKSKVGVAEHSAKLNVYGLPYIRQMEKKAIVA GETLIVTCPVAGYPIDSIVWERDNRALPINRKQKVFPNGTLIIENVERNSDQATYTCVAK NQEGYSARGSLEVQVMVPPQVVPFDFGEETINMNDMVSATCTVNKGDTPLELYWTTAPDP TTGVGRLMSNDGILITKTTQRISMLSIESVHARHRANYTCVARNAAGVIYHTAELRVNVP PRWILEPTDKAFAQGSDAKVECKADGFPKPQVTWKKAVGDTPGEYKDLKKSDNIRVEEGT LHVDNIQKTNEGYYLCEAINGIGSGLSAVIMISVQAPPEFTEKLRNQTARRGEPAVLQCE AKGEKPIGILWNMNNMRLDPKNDNRYTIREEILSTGVMSSLSIKRTERSDSALFTCVATN AFGSDDASINMIVQEVPEMPYALKVLDKSGRSVQLSWAQPYDGNSPLDRYIIEFKRSRAS WSEIDRVIVPGHTTEAQVQKLSPATTYNIRIVAENAIGTSQSSEAVTIITAEEAPSGKPQ NIKVEPVNQTTMRVTWKPPPRTEWNGEILGYYVGYKLSNTNSSYVFETINFITEEGKEHN LELQNLRVYTQYSVVIQAFNKIGAGPLSEEEKQFTAEGTPSQPPSDTACTTLTSQTIRVG WVSPPLESANGVIKTYKVVYAPSDEWYDETKRHYKKTASSDTVLHGLKKYTNYTMQVLAT TAGGDGVRSVPIHCQTEPDVPEAPTDVKALVMGNAAILVSWRPPAQPNGIITQYTVYSKA EGAETETKTQKVPHYQMSFEATELEKNKPYEFWVTASTTIGEGQQSKSIVAMPSDQVPAK IASFDDTFTATFKEDAKMPCLAVGAPQPEITWKIKGVEFSANDRMRVLPDGSLLIKSVNR QDAGDYSCHAENSIAKDSITHKLIVLAPPQSPHVTLSATTTDALTVKLKPHEGDTAPLHG YTLHYKPEFGEWETSEVSVDSQKHNIEGLLCGSRYQVYATGFNNIGAGEASDILNTRTKG QKPKLPEKPRFIEVSSNSVSLHFKAWKDGGCPMSHFVVESKKRDQIEWNQISNNVKPDNN YVVLDLEPATWYNLRITAHNSAGFTVAEYDFATLTVTGGTIAPSRDLPELSAEDTIRIIL SNLNLVVPVVAALLVIIIAIIVICILRSKGNHHKDDVVYNQTMGPGATLDKRRPDLRDEL GYIAPPNRKLPPVPGSNYNTCDRIKRGRGGLRSNHSTWDPRRNPNLYEELKAPPVPMHGN HYGHAHGNAECHYRHPGMEDEICPYATFHLLGFREEMDPTKAMNFQTFPHQNGHAGPVPG HAGTMLPPGHPGHVHSRSGSQSMPRANRYQRKNSQGGQSSIYTPAPEYDDPANCAEEDQY RRYTRVNSQGGSLYSGPGPEYDDPANCAPEEDQYGSQYGGPYGQPYDHYGSRGSMGRRSI GSARNPGNGSPEPPPPPPRNHDMSNSSFNDSKESNEISEAECDRDHGPRGNYGAVKRSPQ PKDQRTTEEMRKLIERNETGPKQLQLQQANGAGFTAYDTMAV |
| Expert options | defaults |
| Search for mutually exclusive exons | defaults, except "Maximal recursion depth = 1" Enable search! |
| Result |
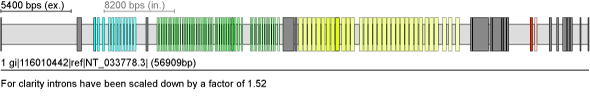
|
| Activity diagrams | Back to top |
Overview of search parameters as activity diagram

|
Detailed diagram of the application flow
|